 CCS includes a number of technologies for capture, transport, and storage of carbon dioxide (CO2) that can be used to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel power generation and other industrial sources. TTPL activates mainly in the modelling of capture and processing/compression of CO2 in order to meet the transportation specifications.
The most mature CO2 capture processes rely on the use of amine solvents to wash CO2 out of the flue gas. Such amines are MEA (monoethanolamine), AMP (2-Amino-2-methyl propanol), MDEA (methyl diethanolamine) and PIPA (Piperazine). The TTPL research involves the investigation and development of thermodynamic models for phase equilibrium and properties predictions for aqueous amine mixtures with CO2 that can be utilized for the selection of amines/amine mixtures for CO2 capture as well as for process simulation purposes.
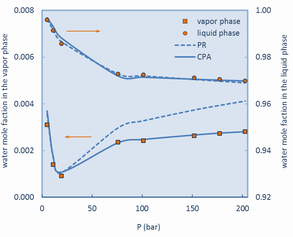
Furthermore, the research of TTPL involves modelling of the CO2 mixtures which constitute the output of the capture process, in order to simulate and optimize the CO2 compression process that follows capture. Modelling is based either on common thermodynamic models, like cubic Equations of State, but also or more advanced models, like the CPA model which has been originally developed in the TTPL and is capable of describing the behaviour of compounds or mixtures with specific interactions (self- or/and across association) like e.g. the CO2/water mixture.
CCS includes a number of technologies for capture, transport, and storage of carbon dioxide (CO2) that can be used to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel power generation and other industrial sources. TTPL activates mainly in the modelling of capture and processing/compression of CO2 in order to meet the transportation specifications.
The most mature CO2 capture processes rely on the use of amine solvents to wash CO2 out of the flue gas. Such amines are MEA (monoethanolamine), AMP (2-Amino-2-methyl propanol), MDEA (methyl diethanolamine) and PIPA (Piperazine). The TTPL research involves the investigation and development of thermodynamic models for phase equilibrium and properties predictions for aqueous amine mixtures with CO2 that can be utilized for the selection of amines/amine mixtures for CO2 capture as well as for process simulation purposes.
Furthermore, the research of TTPL involves modelling of the CO2 mixtures which constitute the output of the capture process, in order to simulate and optimize the CO2 compression process that follows capture. Modelling is based either on common thermodynamic models, like cubic Equations of State, but also or more advanced models, like the CPA model which has been originally developed in the TTPL and is capable of describing the behaviour of compounds or mixtures with specific interactions (self- or/and across association) like e.g. the CO2/water mixture.
Selected publications:
- Pappa G.D., Perakis C., Tsimpanogiannis I.N., Voutsas E.C., Thermodynamic modeling of the vapor-liquid equilibrium of the CO2/H2O mixture, Fluid Phase Equilibria 284(1), 2009, 56-63

